Something You Should Know About Camera Magnet
The exploration of the Art and Science of Photography often fascinates us with the visual appeal of cameras and advanced optical technology. However, equally crucial are the often overlooked subtle and complex mechanical and electronic components within the camera. Specifically, magnets, commonly used in various industrial and everyday devices, play an essential role in the performance of cameras. This article will explore the application of magnets in cameras, covering their purposes, working principles, and practical examples, providing a comprehensive understanding.
The Diverse Role of Magnets in Camera Functions
Core of the Autofocus (AF) System: The camera's autofocus system is controlled using the magnetic field of magnets. Simply put, by altering the current passing through coils, the magnetic field produced by the magnets also changes, which in turn drives the mechanical components of the autofocus system, allowing the lens to move and achieve focus. This process not only needs to be fast but also precise, with the quality of the magnets and the design of the control system being particularly crucial here.
Pillar of the Image Stabilizer (IS/VR): Magnets also hold a place in the optical image stabilization system of cameras. When camera or photographer movement causes image blur, the image stabilizer can automatically adjust the position of the lens or sensor to counteract this movement. Magnets play a role in adjusting the small mechanical components that must move very precisely here, ensuring that the captured photos or videos are clear and stable.
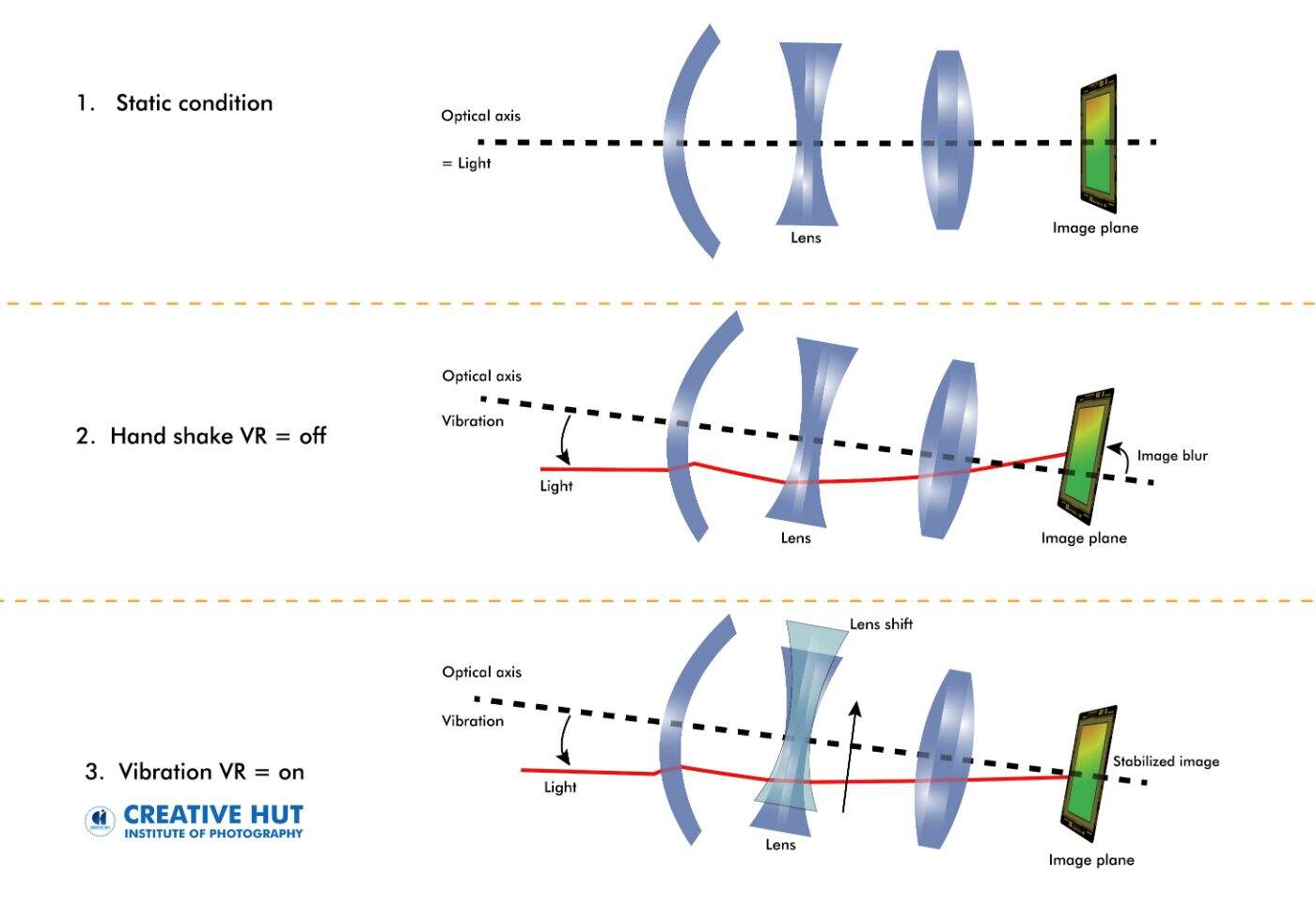
(Photo By: Creative Hut)
Shutter Control: The shutter mechanism in the camera may use magnets to control the opening and closing of the shutter, ensuring accurate exposure time and image clarity when capturing fast-moving objects.

Electronic Viewfinder (EVF): In some electronic viewfinders, magnets can be used to control the display elements inside the viewfinder, ensuring image clarity and stability.

Lens Swap Detection: Some camera systems use magnets to detect whether compatible lenses are installed and automatically adjust camera settings based on lens information.
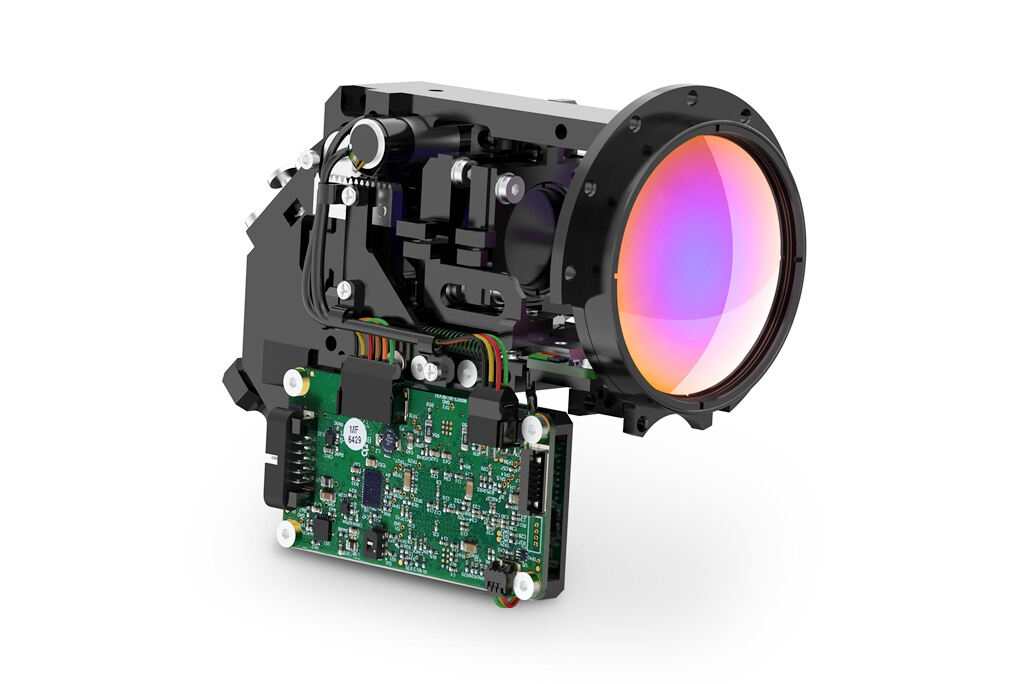

So what does the magnet look like inside the camera? what material and size is it?
NdFeB magnets usually come in various shapes, such as cylindrical, square, ring, etc., as well as various sizes, including diameter, thickness, length, etc. In cameras, the shape and size of these magnets depends on their specific application and design requirements.
For example, in a camera's autofocus system, small but powerful neodymium iron boron magnets are often used to drive the movement of the focusing lens. These magnets may come in cylindrical or square shapes and are smaller in size to fit into tight spaces.
In image stabilizers, NdFeB magnets may have larger sizes and more complex shapes to achieve precise position adjustment and stability control. They may take an annular or composite shape to suit the structural and functional needs of the image stabilizer system.
Understanding How Magnets Work in Practice
The use of magnets in cameras primarily relies on the principles of electromagnetics. This encompasses two essential physical concepts: electromagnetic induction and the Lorentz force.
Electromagnetic Induction Principle: When an electric current flows through a conductor, it generates a magnetic field around the conductor. In cameras, this principle is employed to regulate the strength and orientation of the magnetic field created by magnets. This is achieved by altering the current passing through coils, thereby controlling the mechanical components of the autofocus and lens stabilization systems.
Lorentz Force: The Lorentz force refers to the force that acts on charged particles in response to electromagnetic fields. Within the camera's image stabilization system, the Lorentz force is utilized to precisely adjust the position of the lens or sensor. This adjustment counteracts any movements caused by hand shake or other contributing factors.
Case Study: The Role of Magnets in Enhancing Camera Performance
Let's consider the latest model from a prominent camera brand as a case study and explore how the integration of magnets contributes to the exceptional performance of its autofocus system and optical image stabilization system.
Autofocus System: This camera utilizes small, high-performance magnets and precise current control to achieve rapid and precise autofocus. It excels in tracking fast-moving subjects and operating in low-light conditions, ensuring swift focus adjustments and the capture of clear images.
Optical Image Stabilization System: Through the utilization of carefully controlled magnets, this system dynamically adjusts the lens position during shooting, effectively mitigating image blur caused by hand movement. This functionality is especially critical for shooting with long-focus lenses or in low-light settings.
if you looking for camera magnets? Look no further than AIM Magnet! With 18 years of experience crafting magnets, we uphold the highest quality standards in the industry. Our expertise ensures that you'll get magnets tailored to your exact needs. Plus, with our dedicated production facilities, we can customize shapes and sizes to fit your specifications. Trust AIM Magnet for reliable, top-quality magnets for your camera needs!
Conclusion
Despite their size, magnets hold considerable importance in modern camera technology. Through their scientific utilization, magnets greatly improve the flexibility and image quality of camera shooting, contributing to functions such as autofocus and image stabilization. As technology continues to advance, we anticipate further expansion in the application of magnets and electromagnetics in camera design, promising additional surprises and conveniences.