Motor
In today's modern technology, motors are central to a wide range of devices and machinery, and their function is closely tied to the crucial role of magnets. Magnets are essential to the operation of motors, not only for creating the necessary magnetic field, but also for directly impacting motors' performance, efficiency, and reliability. This article examines the significance of magnets in motors and investigates the usual types and forms of magnets that are commonly utilized.
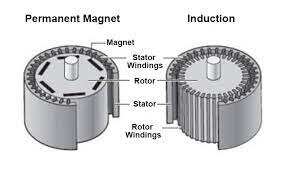
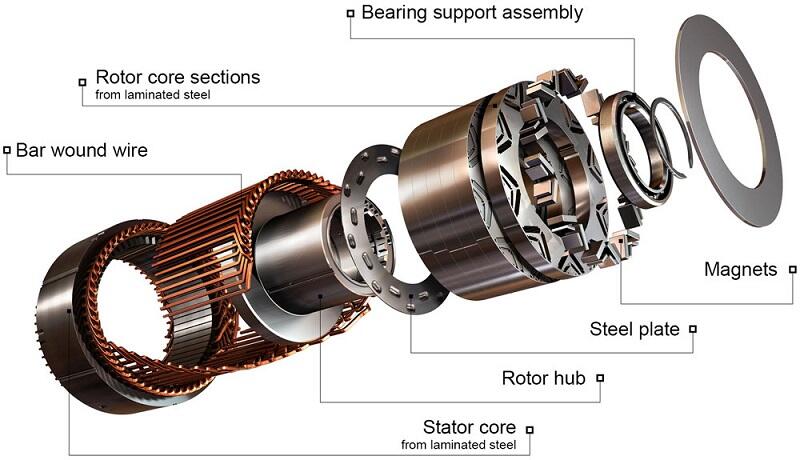
The Vital Importance of Magnets in Motors:
Motors operate on the basic principle of producing torque by leveraging the interplay between current and a magnetic field. Magnets play a crucial role in motors, contributing significantly in three key aspects:
Generation of Magnetic Fields: Magnets, with their distinctive magnetic properties, produce and uphold a robust magnetic field. This field interacts with the current, creating rotational force and propelling mechanical movement.
Sustaining Permanent Magnetism: When functioning as permanent magnets, magnets can maintain their magnetic properties without requiring an external power source. This attribute is especially beneficial for portable devices and small motors.
Boosting Motor Efficiency: High-performance magnets, such as Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB), can dramatically enhance motor efficiency thanks to their higher energy product and more potent magnetic field.
Types of Magnets Typically Found in Motors
Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnets are the most widely used type of magnet in motors. These magnets are preferred for their exceptional magnetic properties and are utilized in various motor designs. Additionally, ferrite and samarium cobalt magnets are employed in certain situations, chosen based on specific requirements and environmental factors.
Typical Magnet Shapes:
Arc Magnets: They are ideal for applications needing a focused magnetic field, such as in motor rotors.
Cylinder Magnets: Commonly employed in motors to create a consistent magnetic field, especially in motor stators.
Block Magnets: Suitable for applications requiring a uniformly distributed magnetic field, such as certain linear motors.
Ring Magnets: Used in applications needing a magnetic field concentrated around a specific point, for instance, in sensors.
In Summary:
In summary, the role of magnets in motors is paramount. Thoughtful selection of magnet types and shapes customized for specific applications is vital for achieving optimal motor performance. Engineers and designers must carefully evaluate magnet properties during the design phase to ensure stable and efficient motor operation across diverse application scenarios. Magnets are not only fundamental to motors; they are a crucial catalyst for technological advancement and innovation.