Magneettisen vetovoiman tutkiminen: magneettien voiman ymmärtäminen
Esittely
Magneetteilla on ratkaiseva rooli erilaisissa sovelluksissa, niin päivittäisistä kotitaloustarvikkeista kuin kehittyneistä teknologisista laitteista. Ne toimivat tärkeimmänä osana magneettista vetovoimaa, joka määrittää magneetin voimakkuuden. Tässä artikkelissa tarkastellaan, mitä magneettinen vetovoima on, miten sitä mitataan ja miksi se on tärkeää. Keskustelemme myös vetovoimaa vaikuttavista tekijöistä, tämän magneettisen ominaisuuden käytännön sovelluksista ja vinkkeistä oikean magneetin valitsemiseksi vetovoiman vaatimusten perusteella.
Mikä on magneettinen vetovoima?
Magneettinen vetovoima tarkoittaa sitä voimakkuutta, jota magneetti voi käyttää ferromagneettiseen materiaaliin (kuten rautaan) niiden ollessa suoraan kosketuksissa. Se mittaa magneetin voimakkuuden ja sen kyvyn pitää tai nostaa esineitä. Mitä voimakkaampi magneettinen vetovoima, sitä voimakkaampi magneetti on.
Miten magneettinen vetovoima mitataan?
Magneetin vetovoima mitataan käyttämällä vetovoimatulosta. Tämä työkalu mittaa magneetin irtautumiseen ferromagneettisesta pinnasta tarvittavan voiman määrän. Luku annetaan yleensä punnissa (lb) tai kilogrammissa (kg). Magneetin tarkoituksenmukaisen käytön varmistamiseksi on välttämätöntä mitata vetovoima tarkasti.
Vaiheet magneettisen vetovoiman mittaamiseksi:
- Valmistelu : Varmista, että sekä magneetti että ferromagneettinen materiaali ovat puhtaita ja ilman mittaukseen vaikuttavia roskia tai pölyä.
- asennus : Aseta magneetti suoraan kosketukseen ferromagneettisen materiaalin kanssa, jotta kosketusalue on mahdollisimman suuri.
- Vetovoiman mittauslaitteen käyttö Liitä vetovoiman mittauslaite magneettiin. Vedä mittausta vähitellen, kunnes magneetti irtoaa materiaalista.
- Mittauksen lukeminen : Huomaa vetovoiman mittauksen lukema, joka osoittaa magneetin enimmäisvetovoiman.
Magneettien ammattimaiseen tuotantoon käytettävän vetovoimantestajan käyttö
Ammattimaisen magneettimestarin on tärkeää varmistaa, että jokainen magneetti täyttää määritellyt vetovoiman vaatimukset. Tämä saavutetaan käyttämällä erikoistunutta välinettä, jota kutsutaan vetovoiman testaajaksi. Vetovoiman testaaja analysoi yksityiskohtaisesti magneetin lujuutta luomalla laajan voimakäyrän, mikä auttaa tunnistamaan magneetin katkaisupisteen. Tämä katkokeski osoittaa, mihin voimakkuuteen magneetti voi kestää ennen kuin se irtoaa ferromagneettisesta materiaalista.
Vetovoimatestaaja varmistaa magneettien vaatimustenmukaisuuden ja auttaa myös laadunvalvonnassa varmistamalla eräiden yhdenmukaisuuden. Kun valmistajat ymmärtävät voimakäyrän, he voivat tehdä tarvittavat mukautukset tuotantoprosessiin magneettisen suorituskyvyn parantamiseksi.
Maagneettisen vetovoiman vaikuttavat tekijät
Magneetin vetovoimaan vaikuttaa useita tekijöitä:
- Materiaalien koostumus : Magneetin valmistuksen laatu vaikuttaa merkittävästi. Neodyymimagneetit ovat esimerkiksi vahvimmista pysyvistä magneeteista, koska ne on valmistettu neodymista, rautaa ja booria.
- Pinta-ala : Magneetin ja ferromagneettisen materiaalin välinen kosketusalue vaikuttaa vetovoimaan. Suurempi pinta-ala johtaa voimakkaampaan vetovoimaan.
- Etäisyys : Magneetin vetovoima vähenee magneetin ja esineen välisen etäisyyden kasvaessa. Tämä johtuu magneettisuuden päinvastaisesta neliölainasta, jonka mukaan magneettinen voima vähenee etäisyyden neliön mukaan.
- Lämpötila : Magneetit voivat menettää voimansa altistuessaan korkeille lämpötiloille. Esimerkiksi neodymimmagneetit alkavat menettää magneettiset ominaisuutensa yli 80 °C:n lämpötilassa.
- Pinnat ja pinnoite : Magneetin pinnoitteen laatu ja pintojen sileys voivat vaikuttaa vetovoimaan. Hillittömämpi pinta varmistaa paremman kosketuksen ja lisää siten vetovoimaa.
Magneettiset materiaalit ja niiden vetovoimat
Eri magneettiset materiaalit osoittavat erilaiset vetovoimat ainutlaatuisen koostumuksensa vuoksi:

- Neodyymi (NdFeB) : Neodyymimagneetit ovat tunnettuja poikkeuksellisesta lujuudestaan ja niiden vetovoima on suuri, joten ne soveltuvat vaativiin sovelluksiin, kuten moottoreihin, lääkinnällisiin laitteisiin ja teollisiin koneisiin.
- samariumkobolti (smco) : Nämä magneetit antavat voimakkaan vetovoiman ja ovat erittäin kestäviä lämpötilan vaihteluihin ja korroosioon. Ne ovat ihanteellisia sovelluksiin, joissa tarvitaan vakautta äärimmäisissä olosuhteissa.
- Alnico : Alniko-magneetit, jotka koostuvat alumiinista, nikkelistä ja kobolttista, antavat kohtuullisen vetovoiman ja niitä käytetään usein antureissa, laitteissa ja kaiuttimissa.
- Keramiikka (ferriitti) : Keramiikkamagneetit vetävät vähemmän kuin harvinaismaagneetit, mutta ne ovat kustannustehokkaita ja niitä käytetään laajalti jokapäiväisissä sovelluksissa, kuten jääkaappi-magneetteissa ja magneettisiteissä.
Magneetteille käytettyjen pinnoitteiden merkitys
Magneettipinnoitteet ovat ratkaisevan tärkeitä magneettien kestävyyden ja suorituskyvyn parantamiseksi. Yleisiä pinnoitteita ovat:
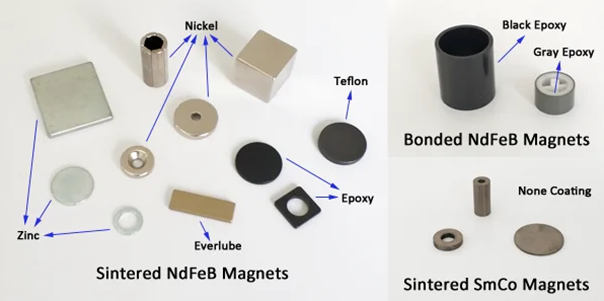
- Kylmäterä : Nikkelipäällysteitä käytetään laajalti neodyymimagneetteja varten. Ne suojaavat erinomaisesti korroosiota ja mekaanista kulumista vastaan, mikä takaa magneetin pitkäikäisyyden.
- Sinkki (Zn) : Sinkkipinnoitteet tarjoavat kustannustehokkaan ratkaisun magneettien suojaamiseksi korroosiolta, erityisesti kosteissa ympäristöissä.
- Epoksi : Epoksypinnoitteet ovat sileät ja kosteuden ja kemikaalien vastustuskykyisiä, joten ne soveltuvat kovissa olosuhteissa käytettäviin magneetteihin.
- Kulta (Au) : Kultapinnoitteet ovat kalliita, mutta ne kestävät korroosiota paremmin ja niitä käytetään sellaisissa käyttötarkoituksissa, joissa magneetin on säilytettävä ennallaan oleva ulkonäkö ja suorituskyky.
Magneettisen vetovoiman käyttö
Magneettien vetovoiman ymmärtäminen ja mittaaminen on ratkaisevaa eri sovelluksissa:
- Teollinen käyttö : Magneetteja käytetään raskaissa koneissa suurten metalliesineiden nostamiseen ja pitämiseen. Vahva vetovoima on välttämätön turvallisuuden ja tehokkuuden varmistamiseksi.
- Lääketieteellinen laitteisto : Lääkintälaitteissa, kuten MRI-laitteissa, käytetään voimakkaita magneetteja, joiden vetovoima on tarkasti kalibroitava.
- Elektroniikka : Puhelinten, kiintolevyjen ja muiden sähkölaitteiden magneetit vaativat erityisiä vetovoiman ominaisuuksia toimivat oikein.
- Kuluttaja-aineet : Päivittäiset esineet, kuten magneettiset solut, puhelinliittymät ja jääkaapin magneetit, tarvitsevat riittävän vetovoiman suorittamaan tarkoituksensa.
- Autoteollisuus : Magneetteja käytetään erilaisissa autoteollisuudessa, kuten antureissa, moottoreissa ja vaihtovälineissä. Vetovoima on optimoitava ajoneuvon osien luotettavan toiminnan varmistamiseksi.
- Uusiutuva energia : Tuuliturbiinit ja muut uusiutuvan energian tekniikat käyttävät voimakasmagneetteja generaattoreissaan. Vetovoima on ratkaiseva tekijä tehokkaan energiamuunnoksen varmistamisessa.
Vinkkejä oikean magneetin valitsemiseksi vetovoiman perusteella
Kun valitset magneetin tiettyyn käyttötarkoitukseen, ota huomioon seuraavat vinkit:
- Määritä vaadittava vetovoima : Määritä, kuinka paljon voimaa tarvitaan. Tämä auttaa sinua valitsemaan magneetin, jonka vahvuus on sopiva.
- Harkitse ympäristöä : Arvioida käyttöolosuhteet, kuten lämpötila, kosteus ja altistuminen kemikaaleille. Valitse magneetti, jolla on sopiva pinnoite, jotta se kestää.
- Koko ja muoto : Magneetin koon ja muodon on vastattava sovelluksen suunnittelun vaatimuksia. Varmista, että magneetti tarjoaa riittävän pinta-alan optimaalisen kosketuksen kannalta.
- Budjettivirheet : Neodyymimagneetit ovat kuitenkin kalliita, vaikka ne tarjoavatkin suurimman vetovoiman. Harkitse kustannusten ja hyötyjen suhdetta ja etsi vaihtoehtoisia materiaaleja, jos budjetti on tiukka.
Johtopäätös
Magneettinen vetovoima on tärkeä parametri, joka määrittää magneetin tehokkuuden ja käytön. Ymmärtämällä vetovoimaa vaikuttavat tekijät ja miten sitä voidaan mitata tarkasti, voi valita oikean magneetin mihin tahansa käyttötarkoitukseen. Olipa kyseessä sitten teollisuuskoneet, lääkinnälliset laitteet, elektroniikka tai päivittäiset kuluttaja-aineet, oikea magneetti, jolla on sopiva vetovoima, takaa optimaalisen suorituskyvyn ja luotettavuuden.