Magnetic Direction
Magnet Magnetization
Magnets are an integral part of modern technology and they play a key role in a variety of applications. Among them, neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) magnets are famous for their strong magnetic properties. However, the performance of NdFeB magnets depends on the magnetization direction, which is a crucial factor. In this article, we will explore what magnetization direction is and its effect on NdFeB magnets.
What Is Magnetization Direction?
Magnetization direction, also known as magnetization orientation or magnetic orientation, refers to the direction in which a magnetic field is applied to a magnet during its manufacture or use. Specifically, it dictates the alignment of the microscopic magnetic moments within the magnet when an external magnetic field is applied. This direction determines the magnet's performance.
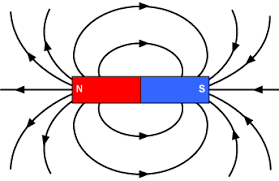
Why Is Magnetization Direction Important?
The magnetization direction has a significant influence on the performance of NdFeB magnets, including the magnetic energy product, residual magnetic induction, and coercivity. Choosing the correct magnetization direction can maximize a magnet's performance, while an incorrect choice may result in decreased performance.
Typical Magnetization Directions
NdFeB magnets typically have three common magnetization directions:
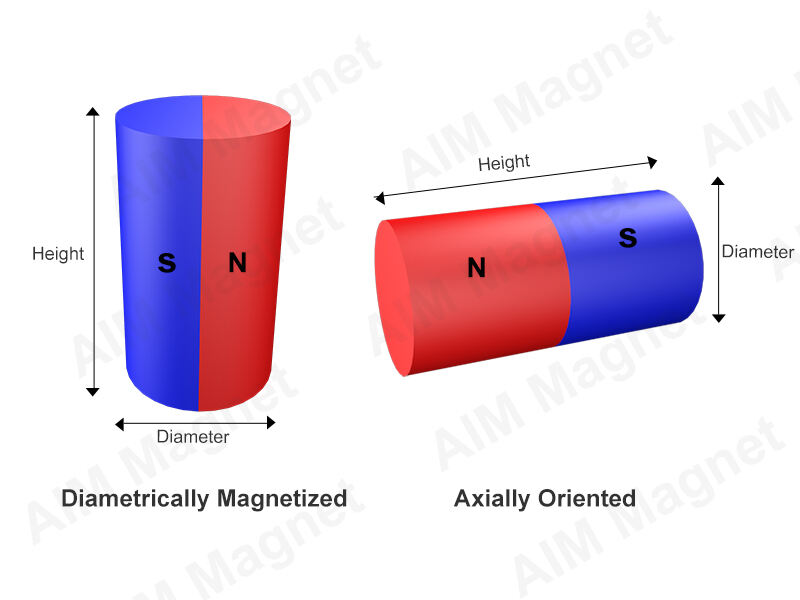
Axial Magnetization:This involves applying the magnetic field along themagnet's axial direction. Axial magnetization is often used in the production ofcylindricalorannularmagnets. It can yield a high magnetic energy product and residual magnetic induction, making it suitable for numerous applications, such as motors and generators.
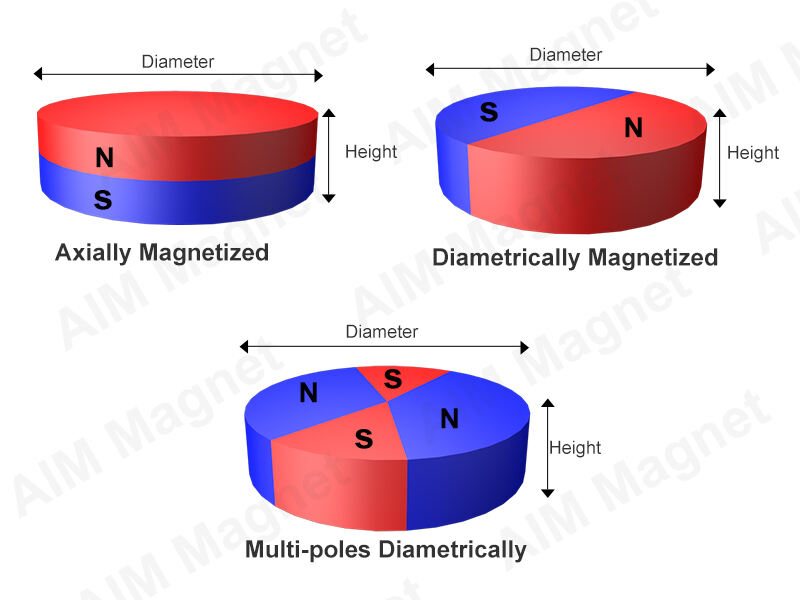
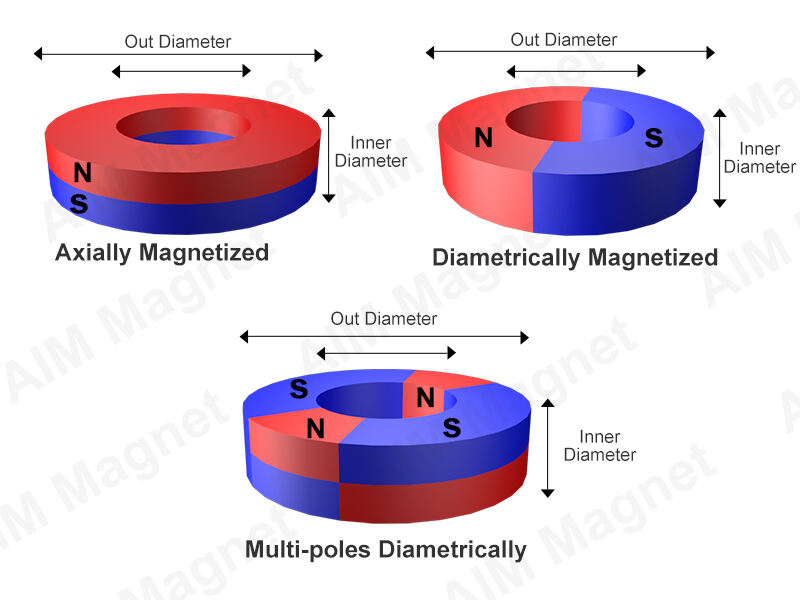
Diametrical Magnetization Direction:Diametrical magnetization direction refers to the magnetization orientation in which the magnetic field runs perpendicular to the diameter of a cylindrical magnet, with North and South poles on opposite sides. It's commonly used in applications requiring a radial magnetic field.
Radial Magnetization:Radial magnetization entails applying the magnetic field from the center of the magnet outward, perpendicular to the axial direction. It is commonly used in the production ofdisk-shaped or ring-shaped magnets. This approach is typically employed in special applications like medical devices and certain sensors.
Selecting the Right Magnetization Direction
Choosing the correct magnetization direction is crucial for a specific application. Engineers typically determine the magnetization direction based on the requirements of the particular application to optimize performance. When manufacturing and using NdFeB magnets, the following factors must be considered:
The desired magnetic performance parameters, such as magnetic energy product, residual magnetic induction, and coercivity.
The geometric shape of the magnet.
The specific applications for which the magnet will be used, such as motors, sensors, or medical devices.